The DOVE scheme was designed to automatically couple different overlapping domains so as to assemble one composite computational domain. This technique can be used to construct computational domains of a complex topology, or as an alternative technique to domain decomposition, commonly used for parallel implementation on distributed memory computer platforms.
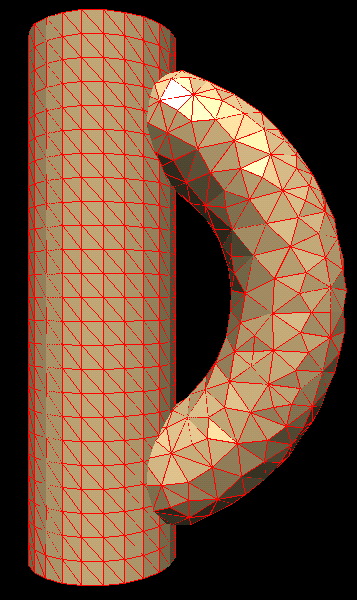
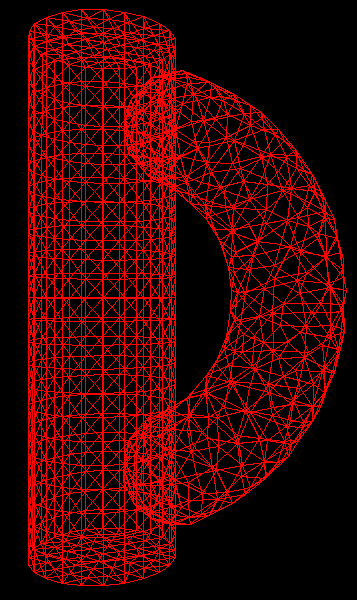
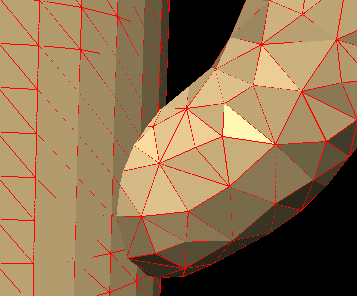
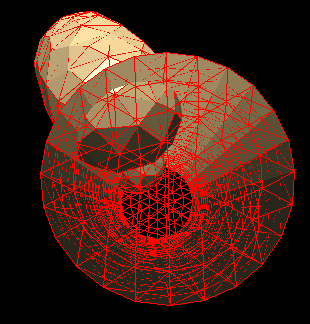
The different domains can be originally created using any unstructured grid generator, or MulPhys native TAM grid generator, based on the patented tool-assisted mesh generation algorithm. After that the dove-algorithm will identify the overlapping regions and sew-together the domains at these regions, so that they will represent one composite domain with the appropriate exchange of variables in the overlapping regions.
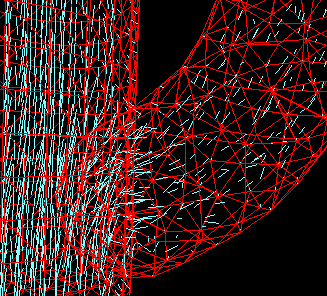
Here is an example of a flow in a duct consisting of two overlapping domains. After the application of the dove algorithm the flow solvers in both domains can exchange information on the flow-variables in the overlapping regions, thus realizing a continuous solution in the total domain.
author={Smirnov, A.V.},
title={Domain coupling with the {DOVE} scheme},
booktitle={Parallel Computational Fluid Dynamics:
Advanced numerical methods, software and applications},
editor={Chetverushkin, B.},
publisher={Elsevier},
address={North-Holland, Amsterdam},
pages={119-127},
ISBN={0-444-51612-3},
year=2004